Key Takeaways:
- An atom is the smallest particle of an element that maintains its chemical identity through all chemical and physical changes.
- An elements is a pure substance which cannot be split into two or more simpler substances by any known chemical means.
- A compounds is a pure substance that is made up of two or more elements chemically combined.
- A molecule is the smallest particle of an element or a compound that can exist separately (or in its own).
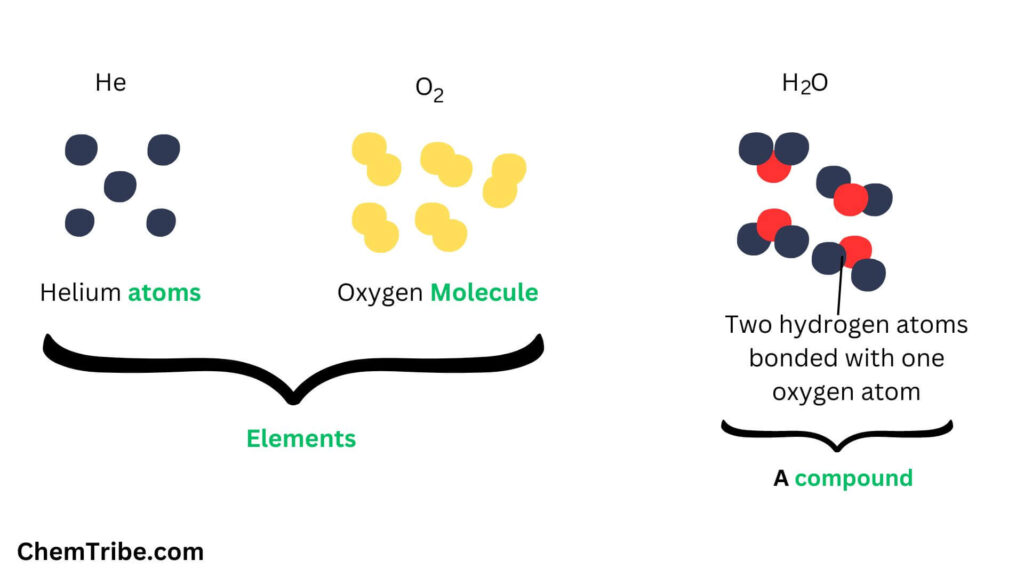
In our past posts on matter, we learnt that matter exists as pure substances and mixtures. The pure substances can further be classified into elements and compounds. The elements comprise over 100 pure substances that are unique because they cannot be further broken down into simpler substances. All other pure substances (numbering in the thousands) can be broken down into two or more substances and are therefore classified as compounds.
What exactly is an element or a compound? What about an atom and a molecule?
Elements and Compounds
In electrolysis of water, which involves passing an electric through water, water is decomposed (or broken down chemically) into two gases: hydrogen and oxygen. The reaction can be represented as follows:
Water → hydrogen gas + oxygen gas
From the above reaction, we can see that water can be broken down into two new substances: Hydrogen and oxygen. Substances like water, which can be broken down into two or more new substances are what are called compounds.
Both hydrogen and oxygen have unique properties that are different from those of water. And unlike water, they cannot be broken down further into new substances by any known chemical means. Such substances like hydrogen and oxygen, which cannot be broken down further into simpler substances are called elements.
With these facts in mind, we can now define elements and compounds as:
Elements are pure substances which cannot be split into two or more simpler substances by any known chemical means.
Compounds are pure substances that are made up of two or more elements chemically combined.
Examples of elements include oxygen, hydrogen, carbon, Sulphur, copper, iron etc. Examples of compounds include sodium chloride, calcium nitrate, Iron (II) sulphide, copper (II) sulphate, potassium chlorate etc.
Atoms and Molecules
We understand that substances are made up of tiny particles. But what are the identity of these tiny particles? The short answer is that they are either atoms or molecules. The next question that you are probably asking is: what are atoms and molecules?
Well, the word “atom” originated from the ancient Greek word “atomos,” which means “indivisible” or “uncuttable.” This term was coined by the ancient Greek philosopher, Democritus in the 5th century BCE. Democritus proposed that all matter is composed of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms that are in constant motion and combine to form different substances. Although Democritus’ atomic theory was largely philosophical and lacked empirical evidence, the term “atom” has persisted and evolved over time, eventually becoming a fundamental concept in modern chemistry and physics.
The existence of atoms is fully accepted by modern scientist and are believed to be the basic building blocks of all matter. Several scientists throughout history have expanded upon the original ideas of atoms.
- John Dalton, in the early 19th century, introduced the concept of atomic theory, proposing that atoms are indivisible and combine in simple whole number ratios.
- Dmitri Mendeleev developed the periodic table in the late 19th century, and organized elements based on atomic mass and properties.
- In the early 20th century, Ernest Rutherford discovered the nucleus of an atom, leading to the model of the atom with a central nucleus orbited by electrons. The concept was further refined by Niels Bohr.
- Subsequent work by scientists such as Werner Heisenberg and Erwin Schrödinger contributed to the development of quantum mechanics, and revolutionized our understanding of atomic structure and behavior.
Drawing from these contributions, scientists formulated a simple and clear definition of the atom as follows:
An atom is the smallest particle of an element that maintains its chemical identity through all chemical and physical changes.
Atoms of some elements are not stable at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. As such, they cannot exist independently but combine with other atoms to form stable complexes, which are made up of two or more atoms. Such stable complexes are what are referred to as molecules.
For instance, two oxygen atoms combine to form an oxygen molecule.
Oxygen atom + Oxygen atom → Oxygen molecule
Apart from oxygen, several other elements as molecules consisting of a pair of atoms, including hydrogen, nitrogen, iodine, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc. Atoms in a molecule are held together by chemical bonds, which are strong forces of attraction between two or more atoms that keep them together so that they are not easily broken down into individual atoms.
Compounds are also made up of molecules. However, in their case, the molecules are made up of two or more different atoms chemically combined together. A molecule of water, for instance, consist of two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen. A molecule of sodium chloride consist of one atom of sodium and one atom of chlorine.
A molecule can, therefore, be defined as follows:
A molecule is the smallest particle of an element or a compound that can exist separately (or in its own).



