Key Takeaways:
- Burettes are typically used to measure precise, variable volumes of liquids.
- Pipettes are designed to measure and transfer specific volumes of liquids with precision.
- Pipettes are more accurate than burettes when it comes to releasing smaller volumes of liquids.
- Volumetric pipettes are more accurate than graduated pipettes and burettes because they are designed to deliver a fixed volume of liquid with high precision.
In the laboratory, precise measurement and transfer of liquids are essential for accurate experimental results. Two common tools for this purpose are the burette and the pipette. While you can use both to measure accurate volumes of liquids, they offer unique advantages as far as precision levels are concerned.
So, which apparatus is more precise? Let’s find out…
Burettes
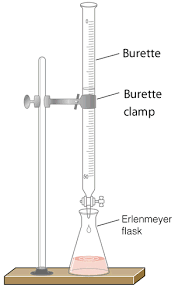
Burettes are long, thin glass tubes with graduated scales along their sides for measuring accurate volumes of liquids. They feature stopcocks at the bottom to control how fast the liquid is dispensed. The glass tube usually has tapered ends to facilitate accurate dispensing of the liquid. By turning the stopcock, you can release small amounts of liquid slowly or drop by drop. Burettes are commonly used for dispensing larger volumes of liquids, usually in the range of milliliters to liters and they come in various sizes, such as 25 ml, 50 ml, or 100 ml.
Pipettes
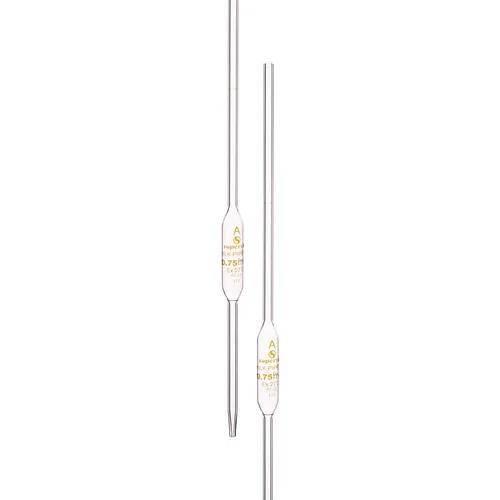
A pipette typically consists of a long, narrow glass with a bulb located in the middle section. This bulb serves as a suction mechanism to draw up the liquid into the pipette. Like the burette, the pipette has tapered ends to facilitate accurate dispensing of the liquid.
Pipettes are designed to measure and transfer specific volumes of liquids with precision, and they often feature markings or hash marks to indicate when they are filled to the desired volume.
There are two main types of pipettes:
- Graduated Pipettes: Also known as Mohr pipettes, they are designed to measure and transfer variable volumes of liquid within a certain range. They have graduations along the length of the pipette, which allows for measurements of different volumes depending on where the liquid is drawn up to. Graduated pipettes are commonly used for general laboratory tasks where precise volume measurements are not as critical. You have to read the meniscus carefully to achieve accurate liquid volume measurements. Their precision also varies with the type, class, and design, which introduces the possibility of human error.
- Volumetric Pipettes: They are designed to measure and transfer a specific, fixed volume of liquid. They are often used when precise volume measurements are required, such as in preparing standard solutions or conducting analytical experiments. Volumetric pipettes typically have a single graduation mark indicating the calibrated volume.
Release Mechanism
Apart from the physical differences we’ve highlighted above, burettes and pipettes differ in their release mechanism. While burettes feature stop cocks for controlling the amount of liquid that they dispense, pipettes have dropper-like mechanisms that release the measured liquid by reducing the vacuum in the bulb.
Precision
Generally, burettes are typically used to measure precise, variable volumes of liquids. Because the liquid travels a long distance for a small volume, a burette can deliver RELATIVELY ACCURATE volumes of liquids. But because of they are larger, they dispense higher capacities of liquids than pipettes. As such, they tend to be less accurate than pipettes when it comes to releasing smaller volumes of liquids.
Volumetric pipettes are particularly considered to be more accurate than burettes (they are even more accurate than graduated pipettes). As aforementioned, volumetric pipettes are specifically designed to deliver a fixed volume of liquid with high precision, often to within ±0.1% or better accuracy. They are also calibrated to deliver the specified volume at a specific temperature, typically 20°C.
On the other hand, while burettes can also provide accurate measurements, their accuracy may not be as high as that of volumetric pipettes. Burettes are primarily designed for delivering variable volumes of liquids and may have a stated accuracy of ±0.05 mL or better, depending on the manufacturer and the specific model.
That being said, the accuracy of both burettes and pipettes ultimately depends on factors such as proper technique, calibration, and environmental conditions.
Also check the difference between: Round-Bottomed Flasks and Flat-Bottomed Flasks



