A laboratory is a building or special room specifically designed for conducting experiments, research, and practical demonstrations related to chemical principles and reactions. It is equipped with various equipment (or apparatus) and chemicals necessary for carrying out experiments safely and effectively.
Most laboratory apparatuses that are used as containers or reaction vessels are made with transparent glass or plastic. This is to allow correct observation during a reaction or measurement, for instance, to determine the level of liquids held in there. Glass and plastic also don’t react with most of the reagents used in the laboratory.
Most Common Categories of Laboratory Apparatus
- Apparatus for Heating: Heating sources in the laboratory are needed to facilitate chemical reactions, evaporate liquids, sterilize equipment, melt solids, dry samples, and perform various other essential tasks. The most common apparatus used for heating in the laboratory are the Bunsen burner, hot plates, and spirit lamp.
- Apparatus for Measuring Temperature: Temperature is usually measured with thermometers. The most common types of thermometers in chemistry laboratories are maximum and minimum thermometers, clinical thermometers, and general-purpose thermometers.
- Apparatus for Measuring Mass: Mass is measured using weighing balances. The most common types of weighing balances in chemistry laboratories include beam balances, electronic balances, and top balances.
- Apparatus for Measuring Volume: Apparatus used for measuring volumes of liquids include graduated beakers, graduated conical flasks, measuring cylinders, volumetric flasks, syringes, pipettes, and burettes. Each apparatus is designed for its specific use and may come in various sizes. Graduated beakers, graduated conical flasks, and measuring cylinders are used to measure approximate volumes of liquids. When fairly accurate volumes are required, volumetric flasks, syringes, pipettes, and burettes are used.
Names and Uses of Various Laboratory Apparatus
Let’s now focus on specific laboratory apparatus and their uses. There are many laboratory apparatuses that you will find in modern chemistry laboratories but here is a list of the most common:
4. Round-Bottomed Flask
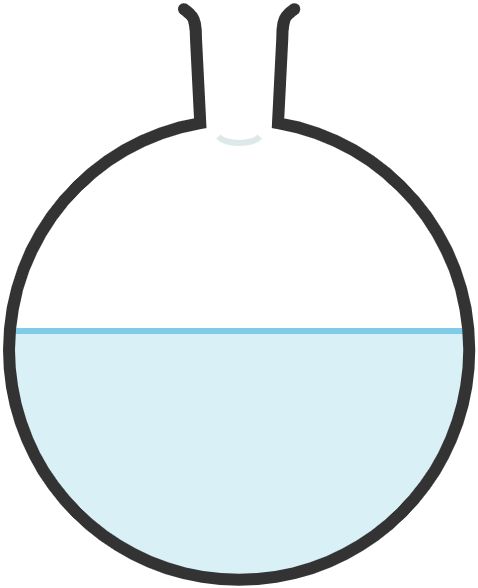
Used when heating liquid substances because heat is supplied uniformly so that the flask doesn’t crack as it expands
6. Conical Flask
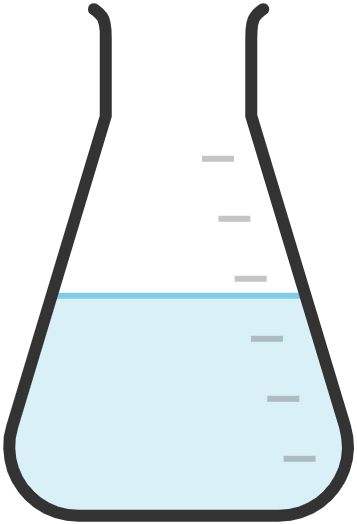
Used for general laboratory experiments and for measuring approximate volumes of liquids
7. Filter Funnel
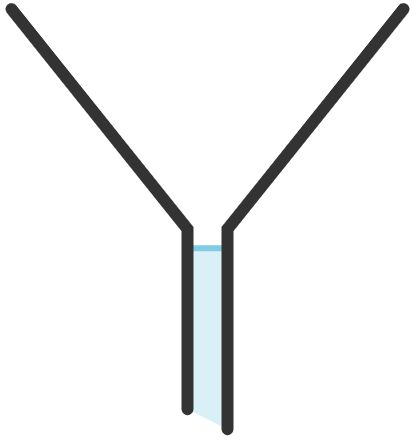
Used for delivering liquids carefully into vessels
8. Dropping Funnel

Used to add controlled amounts of liquids into reaction funnels
9. Separating Funnel
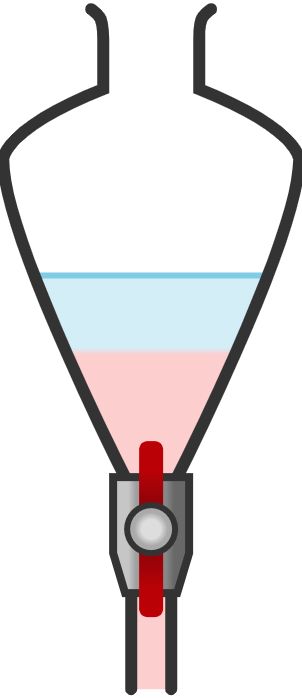
Used for separating immiscible liquids
10. Thistle Funnel
Used for delivering liquid substances in reaction vessels
13. Wash Bottle
Used to hold water for rinsing vessels and for adding water to vessels with narrow necks
14. Reagent Bottle
Used for storing bench reagents
15. Spatula

Used for scooping solid substances from containers
19. Teat Pipette (Dropper)

Used for delivering liquids drop-wise
20. Crucible
Used when heating solid substances that require strong heating
21. Desiccator
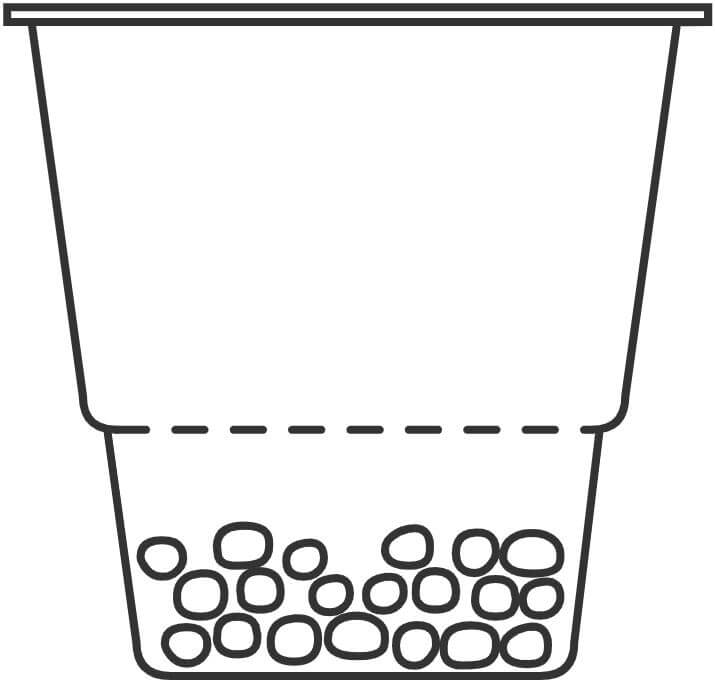
Used for drying or keeping substances free from moisture
22. Pipe-clay triangle
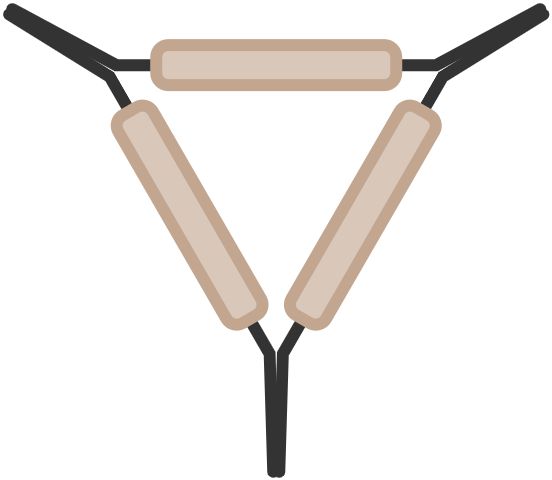
Used for supporting crucibles during heating
23. Bunsen Burner
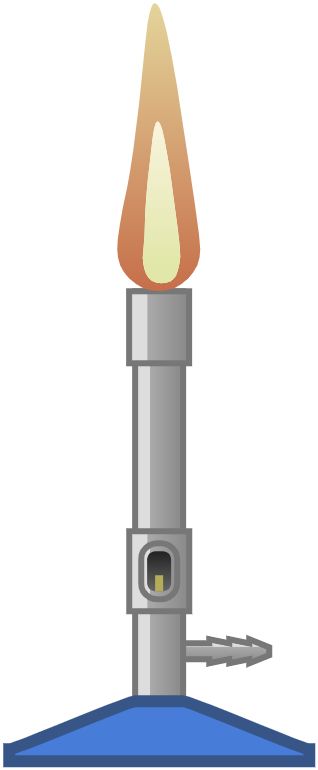
Source of heat in the laboratory
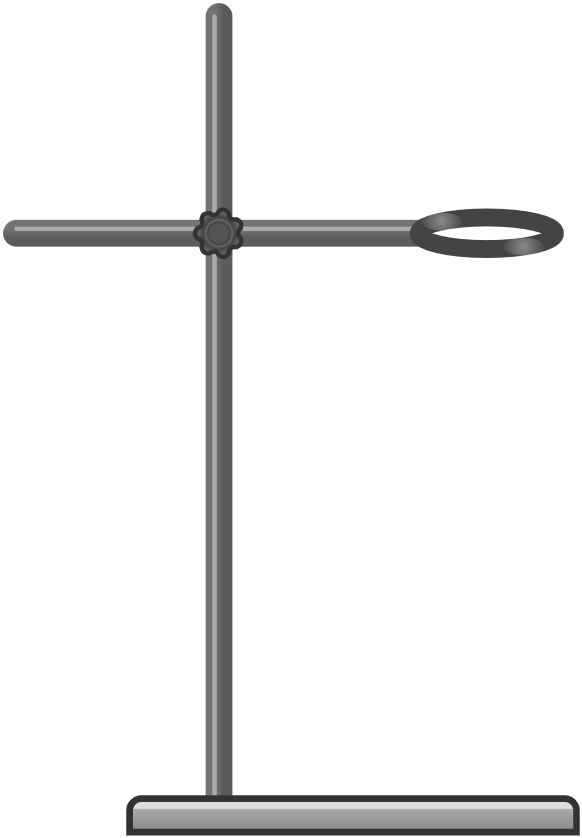
24. Tripod Stand
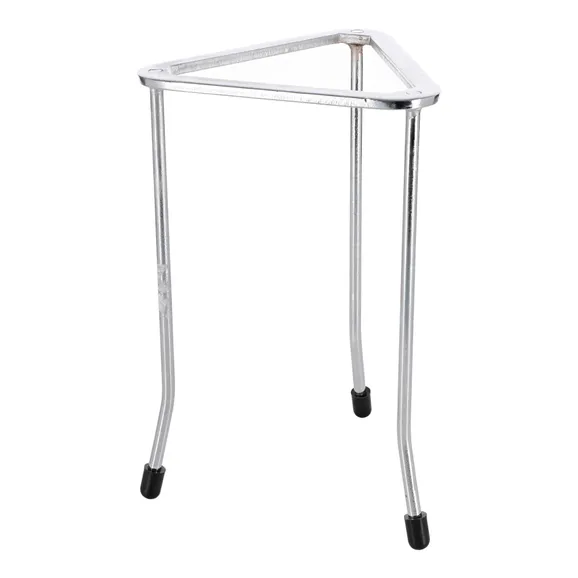

Used for supporting beakers and flasks during heating
25. Wire Gauze
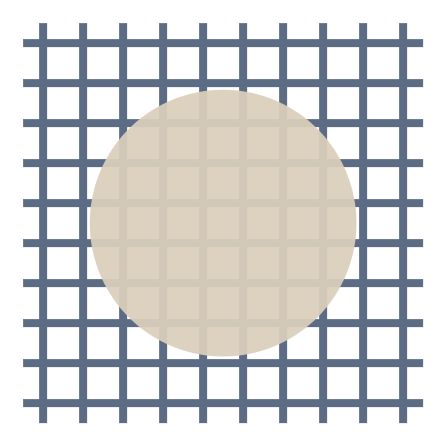
Used for even distribution of heat when heating substances in beakers or flasks
26. Mortar and Pestle
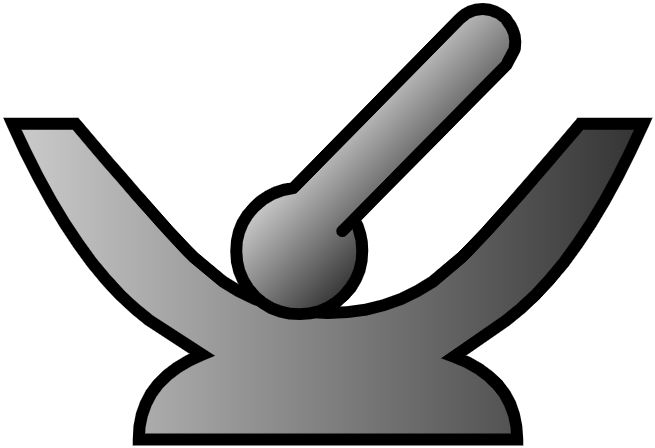

Used for crushing substances
30. Watch glass

Used as a surface to evaporate a liquid, as a cover for a beaker, to hold solids while being weighed, and for heating a small amount of substances.
31. Spotting Tile
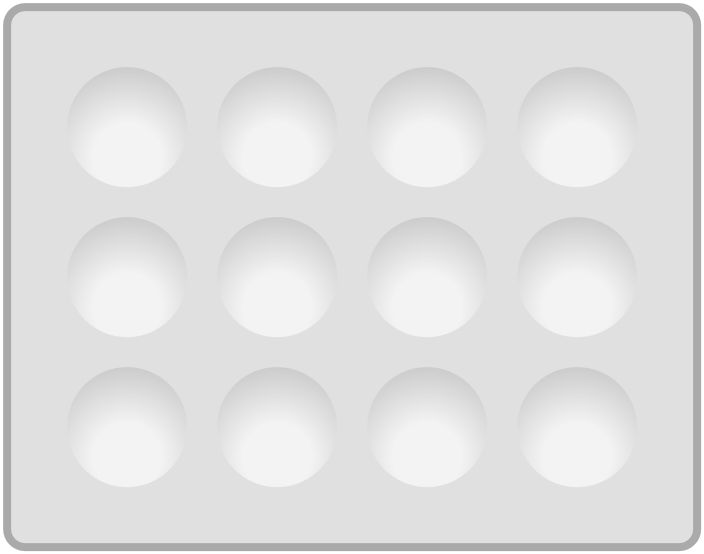
Used to observe color changes in micro quantities of liquids
32. Schlenk flask
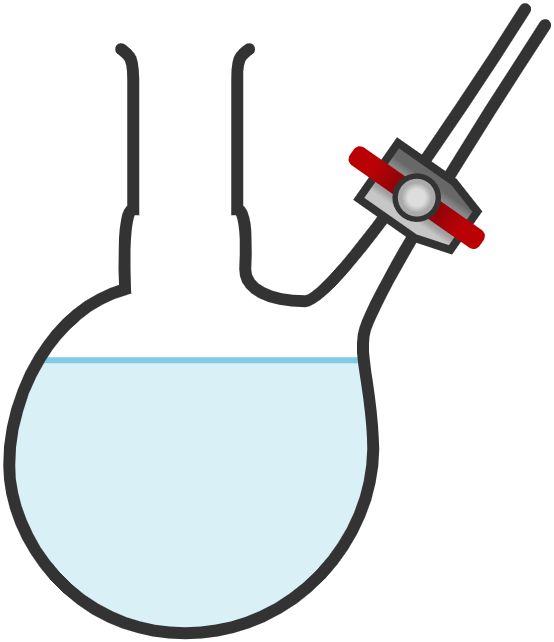
Used to handle air-sensitive reagents without exposing them to oxygen or moisture
33. Beaker
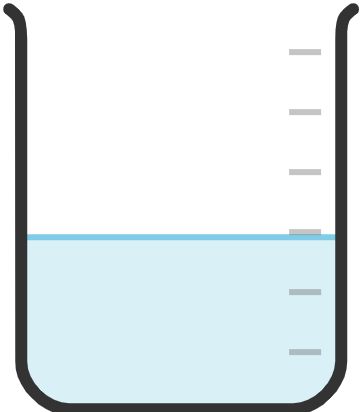
Used for mixing, heating, storing, and measuring liquids, and for general laboratory tasks.
34. Displacement Beaker
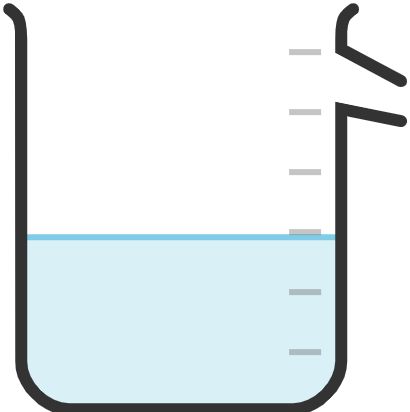
Used to collect and measure the volume of gas evolved during a chemical reaction.
35. Büchner funnel

Used for vacuum filtration
36. Liebig condenser

Used to cool and condense vapors, typically during distillation processes.
37. Fractionating column
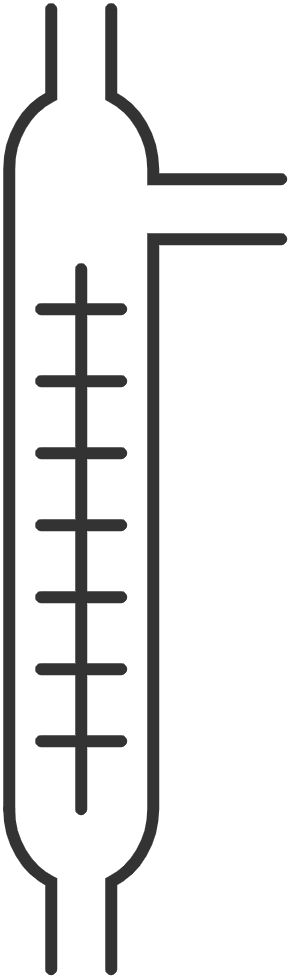
Used during distillation to provide surface area over which vapor condenses before passing into the Liebig condenser.
38. Distillation flask

Used to hold the liquid/mixture being distilled.
39. Distillation head
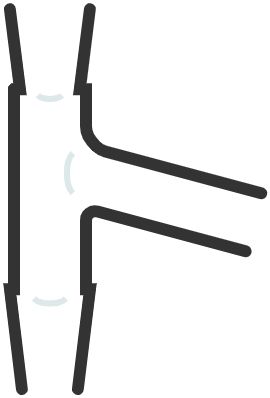
Used to connect the distillation flask to the condenser in a distillation setup.
40. Graduated cylinder
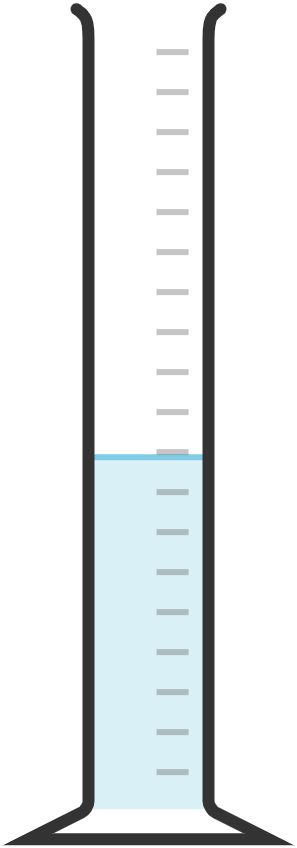
Used to measure volumes of liquids accurately.
41. Stirring rod

Used for stirring solutions and suspensions.
42. Hot plate

Used to heat solutions and substances in the laboratory.
43. Weighing balance
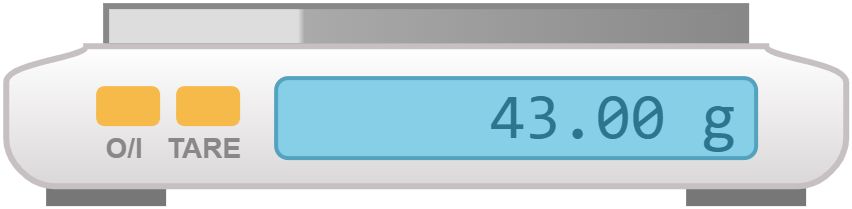
Used to measure the mass of substances accurately.
44. Stopwatch

Used to measure the duration of time intervals in experiments.
45. Thermometer
Used to measure the temperature of substances or solutions.
46. Filter paper
Used to separate solids from liquids through filtration.
47. Magnetic Stir Bar

Used to stir solutions in sealed containers (without the need to open the containers)
48. Lab Vials
Used to hold or store small quantities of laboratory samples.
49. Thiele tube
Used for determining melting and boiling points of substances accurately.
50. Cuvettes
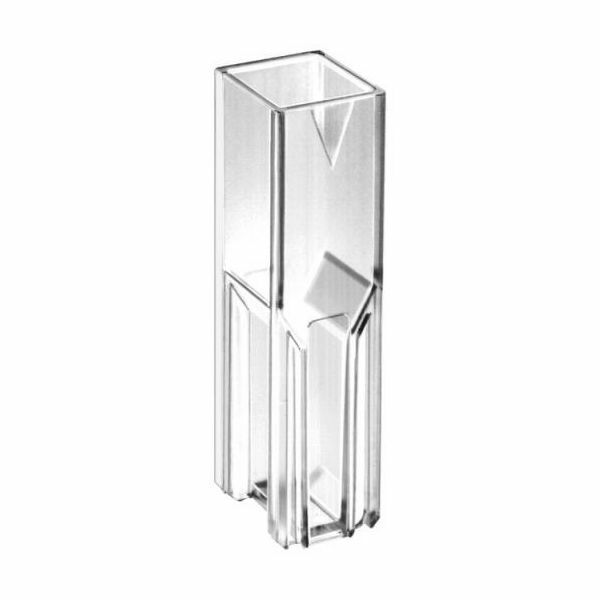

Used to hold samples in spectrophotometry for analysis of light absorption/transmission.
51. Gas syringe
Used to measure the volume of gases produced or consumed in a reaction.
52. Tweezers
Used to handle small objects with precision.
53. Goggles
Used for eye protection against chemical splashes, debris, or other hazards.
54. Rubber tube
Used to transfer liquids or gases between apparatus.
55. pH meter
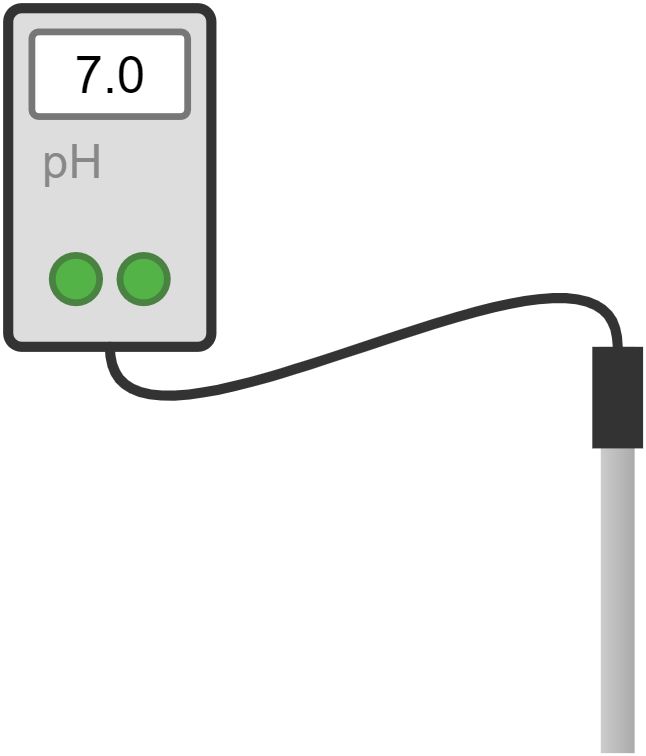
Used to measure the acidity or basicity of a solution.
56. Microscope
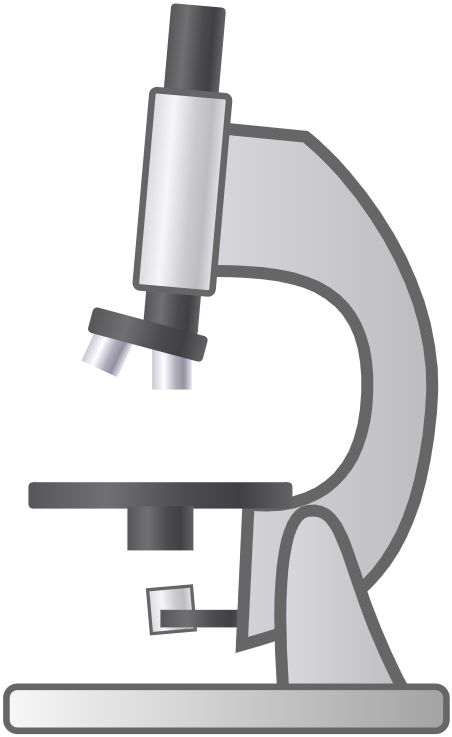
Used to examine small samples of substances (crystals, cells, bacteria etc)
57. Centrifuge Machine
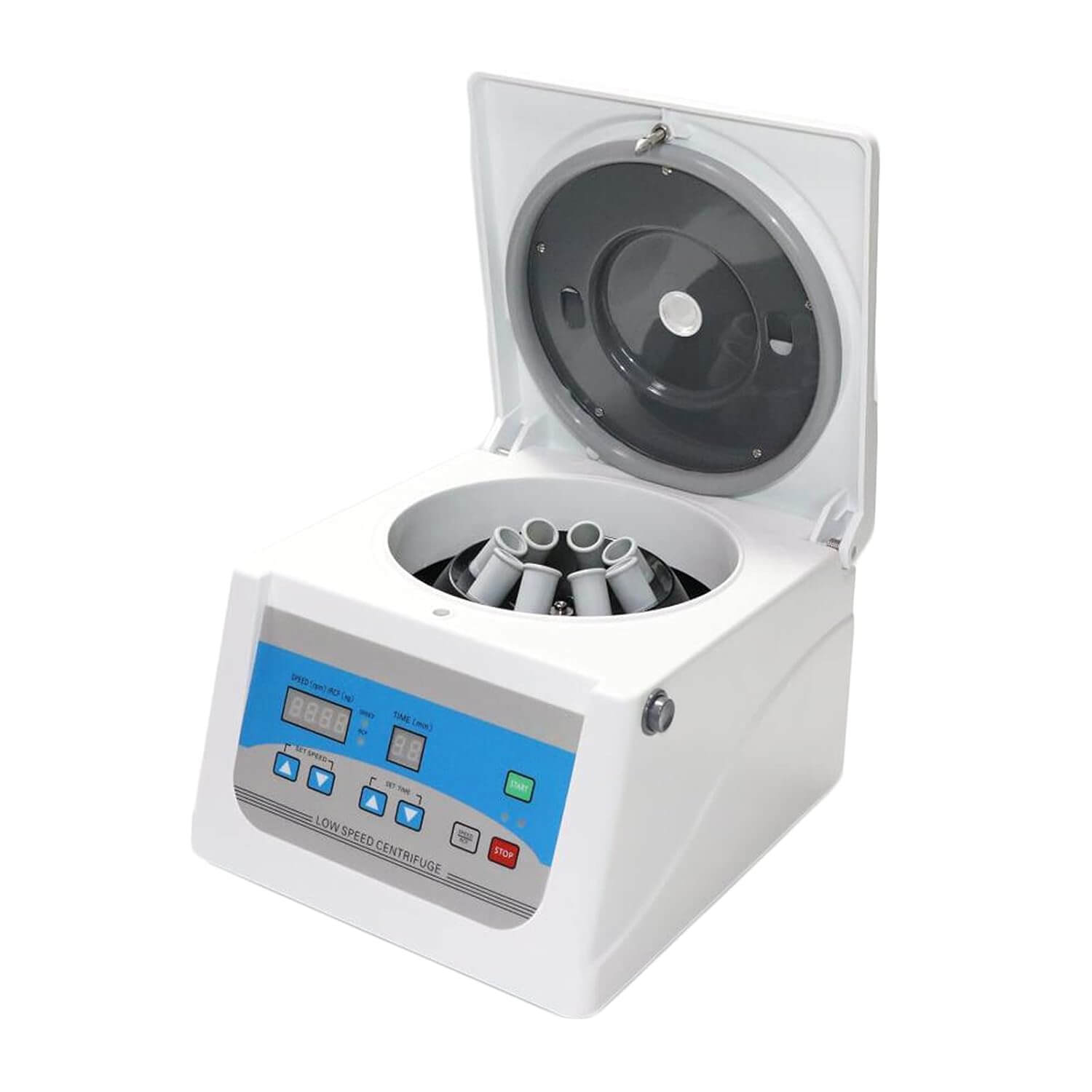

Used to separate components in a mixture based on density through rapid spinning.
59. Büchner Flask/Vacuum Flask)
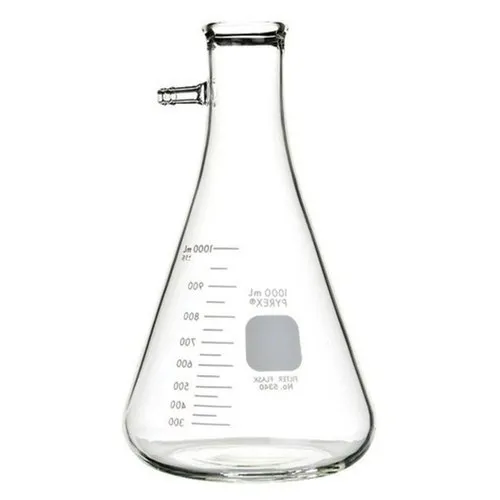

A type of conical flaks used in vacuum filtration, where liquid is drawn through a filter by suction
60. Pressure-Equalizing Dropping Funnel
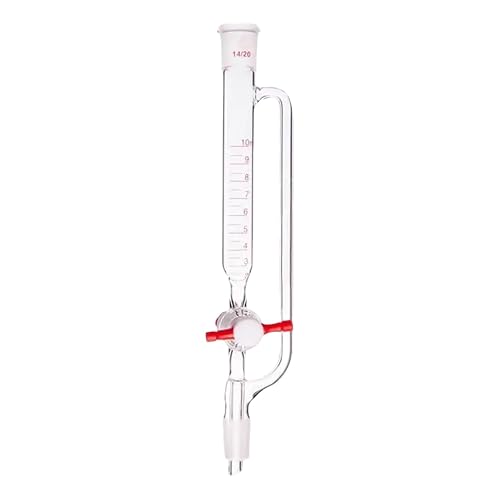

A dropping funnel that maintains equal pressure to allow safe, controlled addition of liquids and prevent backflow.
61. Beehive Shelf
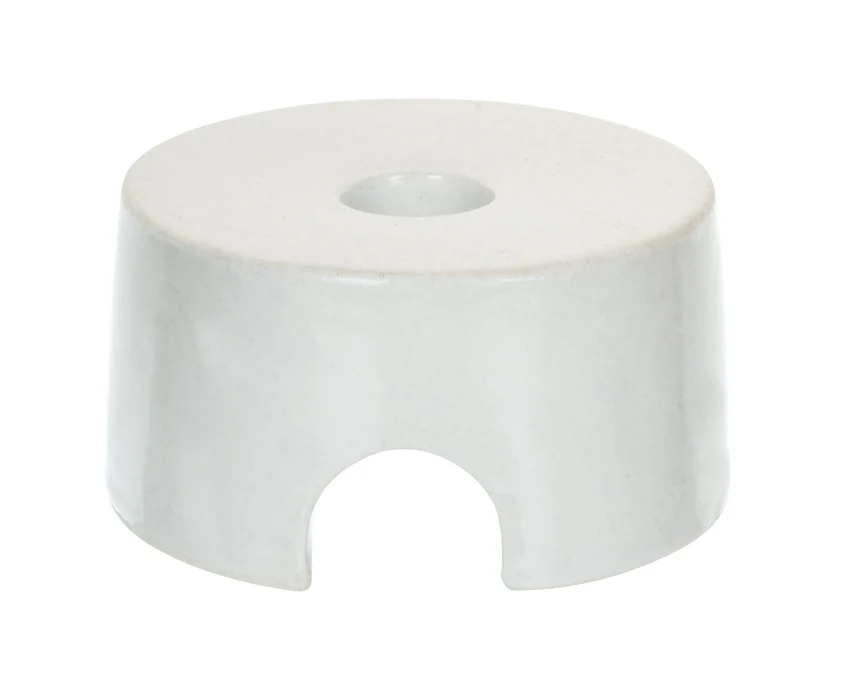

Used to support the gas jar in a pneumatic trough while allowing gas to fill it during collection
This list of laboratory apparatus should serve as a useful starting point for any beginner chemistry student and researcher. However, it’s important to note that the list isn’t exhaustive. Depending on the specific experiments or research being conducted, you may encounter numerous other specialized apparatus.