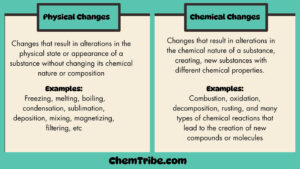
Decantation
Sand is insoluble in water. When you allow a mixture of sand and water to stand, the sand will start to settle at the bottom of the container. After all the sand has settled, you can carefully pour water out into another container with the help of a glass rod, leaving the settled solid sand particles (also called residue) in the original container. By doing this, you would have separated the mixture. This method of separation is what is often referred to as Decantation.
The settling down of particles of the insoluble solid (sand in this case) is called sedimentation. The upper clear liquid is called supernatant. The insoluble solid (sand) is called sediment.
Decantation is commonly used in the separation of insoluble solids from liquids. It can also be used to separate immiscible liquids with different densities. The less dense liquid that settles at the top can be poured off into a different container leaving the denser liquid in the original container.
Decantation is a separation technique used to separate solid-liquid or liquid-liquid mixtures based on the difference in density between the components. In decantation, the mixture is allowed to stand undisturbed until the denser component settles at the bottom, forming a sediment or layer. The less-dense component is then carefully poured off or decanted from the top, leaving the denser component behind.
But decantation has a few limitations:
- In the case of sand and water mixture, for instance, the separation is not efficient because some particles still pass into water in the process of decanting. That’s why the water that you collect in the second container is not clear. It is still composed of small suspended particles of sand.
- Very fine solid particles take long to settle. And any disturbance of the liquid mixes them.
Filtration
The above limitations can be mitigated by using a closely related separation technique called filtration. Unlike decantation, filtration allows you to separate even solids suspended in liquids. It uses a filter through which liquid molecules can pass through easily but solid particles cannot. The most commonly used type of filter in modern chemistry laboratories is filter paper. It contains tiny pores through which permit the passage of liquid molecules while effectively trapping solid particles. The liquid that passes through the filter is called filtrate while the solid that remains is called the residue.
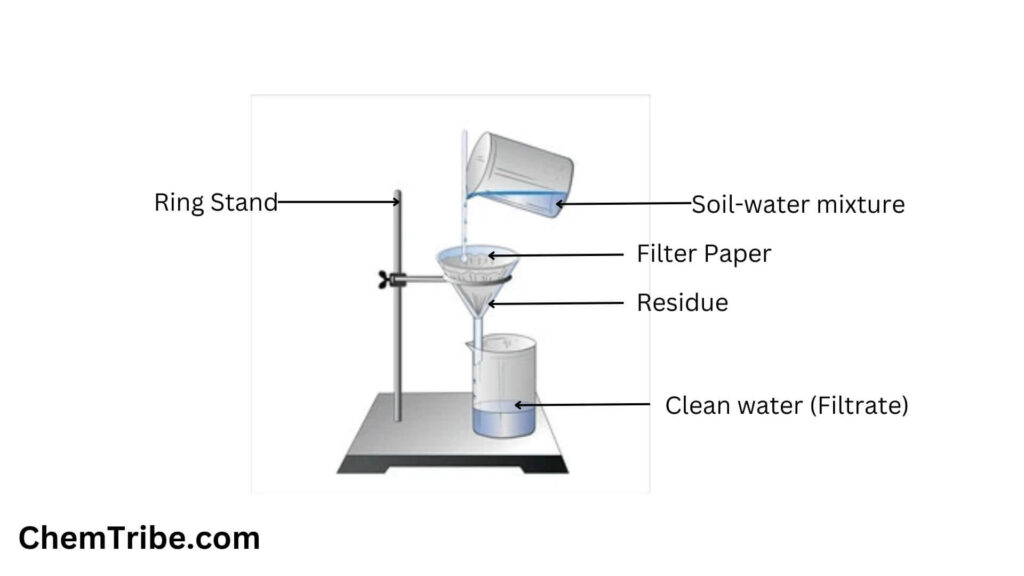
Filtration is a separation technique used to separate solid-liquid mixtures or suspensions by passing them through porous materials, called filters, which selectively allow the liquid to pass through while retaining the solid particles. The mixture is poured or forced through the filter, allowing the liquid (filtrate) to pass through while trapping the solid particles (residue) on the filter.
Filtration is used on a large scale in water purification plants. Dirty water is allowed to pass through a filter bed made of layers of gravel and sand. Suspended particles are trapped by the gravel and sand while the water passes through and comes out as clean water. Domestic water filters use the same principle.
So, the main difference between decantation and filtration is the advantage that the latter provides: the ability to separate even the suspended solids. That said, filtration also has a major disadvantage: it cannot remove dissolved substances. To remove dissolved substances, you may need to use other separation methods like evaporation, distillation, sublimation, solvent extraction, chromatography etc.
Decantation vs Filtration Summary
| Aspect | Decantation | Filtration |
| Process | Mixture is allowed to stand undisturbed until the denser component settles at the bottom. | Mixture is passed through a filter medium, allowing liquid to pass while retaining solid particles. |
| Efficiency | Less effective for very fine particles or colloidal suspensions | More effective for separating fine particles and colloidal suspensions |
| Time | Generally quicker than filtration | May take longer time depending on the volume and nature of the mixture |
| Application | Commonly used for simple separations or preliminary purification | Widely used in various industries and laboratory settings for precise separation |