-
Ring Stands: Uses, Types of Clamps, Areas of Application, & Safety
In chemistry laboratories, ring stands are used to hold and support pieces of apparatus (burettes, beakers, conical flasks, test tubes, funnels, etc.) during experiments. They are also called clamp stands, support stands, or retort stands. As you can see in the diagram 1 above, a ring stand has a heavy base (to make it more…
-
Deflagrating Spoon: Use, Experiments that Require It & Safety Tips
A deflagrating spoon is a long metallic spoon with a vertical handle that is often used in the laboratory to hold substances that are being burned in gas jars. As you can see in the picture below, it typically consists of a long handle with a small cup at the end to hold the sample…
-
Types of Flames in Bunsen Burner
The Bunsen burner is the most common and most convenient heating source in most chemistry laboratories. It was invented by Professor Robert Bunsen in 1855. It consists of three main parts: How a Bunsen burner Works The Bunsen burner is normally connected to an external source of laboratory gas (usually methane) by rubber tubing. The…
-
Common Laboratory Apparatus: Names and Uses
A laboratory is a building or special room specifically designed for conducting experiments, research, and practical demonstrations related to chemical principles and reactions. It is equipped with various equipment (or apparatus) and chemicals necessary for carrying out experiments safely and effectively. Most laboratory apparatuses that are used as containers or reaction vessels are made with…
-
Basic Chemistry Laboratory Safety Rules for Students
The study of chemistry involves conducting numerous experiments, which require the use of various chemicals and pieces of apparatus. These experiments typically take place in a specialized room known as a Laboratory. Thus, a laboratory can be described as a dedicated space or building where chemicals and equipment are stored, and practical subjects like chemistry…
-
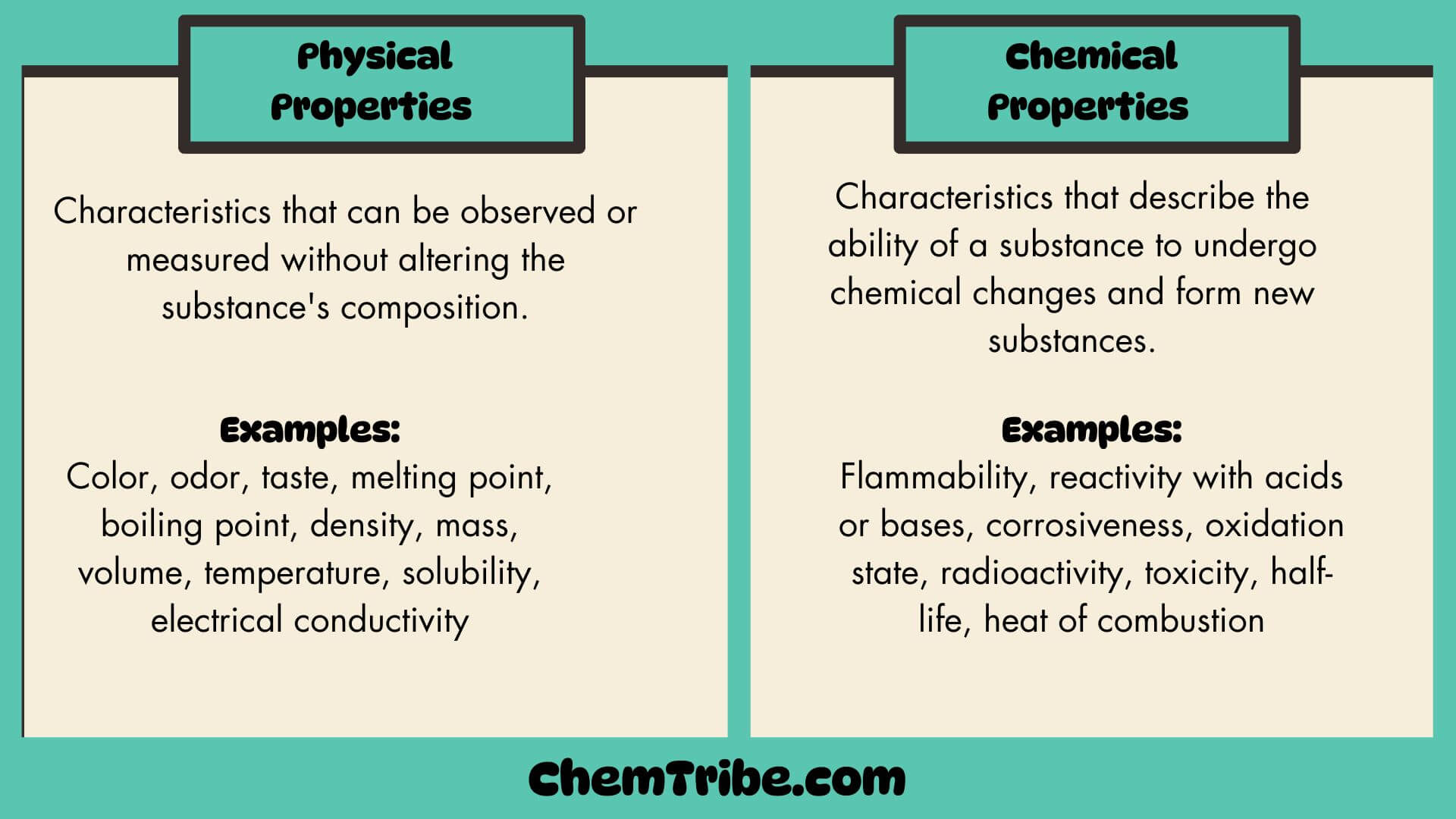
Physical and Chemical Properties of Matter
We have used the terms “physical” and “chemical” properties of substances in previous posts, and we will use them frequently in subsequent posts. Therefore, it is important to understand what they mean in chemistry. Each substance possesses a unique set of properties that distinguishes it from other substances. These properties can be classified into two…
-
Heating and Cooling Curves
What happens to the temperature of a substance when it is heated or cooled? Many students think that temperature increases smoothly from solid to gaseous states but that is not the case. Heating and cooling curves are often used to depict the temperature changes of substances as heat is added or removed over time.…
-
How to Demonstrate That Gases Have Mass
The primary states of matter—solid, liquid, and gas—exhibit distinct properties, which we have explored in this post. Now, let’s revisit the properties of gases. We previously established that “Gases have indefinite shapes and volumes but definite mass.” While we explained why gases have indefinite shapes and volumes, we only briefly mentioned that they have definite…
-
Learn How to Identify States of Matter with These Examples
In this post, we learned that matter exists in three main states depending on environmental conditions like temperature or pressure: solid, liquid, and gaseous states. We also discovered that these three states are not the only ones in which matter can exist; there are also the 4th and 5th states of matter (see previous post).…
-
The Fourth and Fifth States of Matter
In the previous post, we discussed the three primary or conventional states of matter: solid, liquid, and gaseous states. We mentioned that these are not the only states of matter and promised to reveal the other two most important states of matter in chemistry: the 4th and 5th states of matter, plasma and Bose-Einstein condensate…