-
Properties of Acids
We have already learned about the physical properties of acids in this previous post. Let’s now focus on the chemical properties of acids (or how they react with other substances). 1. Reaction of Acids with Metals Acids react with metals to form a salt and hydrogen gas. Acids contain chemically bound hydrogen, which can be…
-
Natural, Commercial, & Universal pH Indicators
In the previous post, we mentioned that one of the properties of acids is that they have sour tastes, while bases have bitter tastes. Using taste to classify substances as acids or bases is not an accurate method. It is not safe either due to the potential harm that acidic or basic substances can cause…
-
Introduction to Acids and Bases
Acids and bases are everywhere. When you squeeze a lemon to make lemonade, the juice is an acid. If your TV remote operates on battery power, the batteries contain acids. Acids flow through our bodies, aiding in food digestion and even facilitating muscle building. And what about bases? Well, if you washed your hands today,…
-
How to Tell Which Elements Are Present in a Compound from Its Name: The Ate, Ite, & Ide Suffixes
In the previous section, we defined a compound as a pure substance made up of two or more elements chemically combined. Given the many ways in which elements can combine, the number of possible compounds is virtually limitless. But how do we name all these compounds? How can we know which elements constitute a compound?…
-
Mixtures and Compounds
In the previous section, we’ve learnt that a compound is a pure substance that is made up of two or more elements chemically combined. We also learnt in previous sections that that matter exists as pure substances and mixtures. So, what is the difference between a mixture and a compound? Well, the difference between a mixture…
-
Atoms, Elements, Molecules, and Compounds
Key Takeaways: In our past posts on matter, we learnt that matter exists as pure substances and mixtures. The pure substances can further be classified into elements and compounds. The elements comprise over 100 pure substances that are unique because they cannot be further broken down into simpler substances. All other pure substances (numbering in…
-
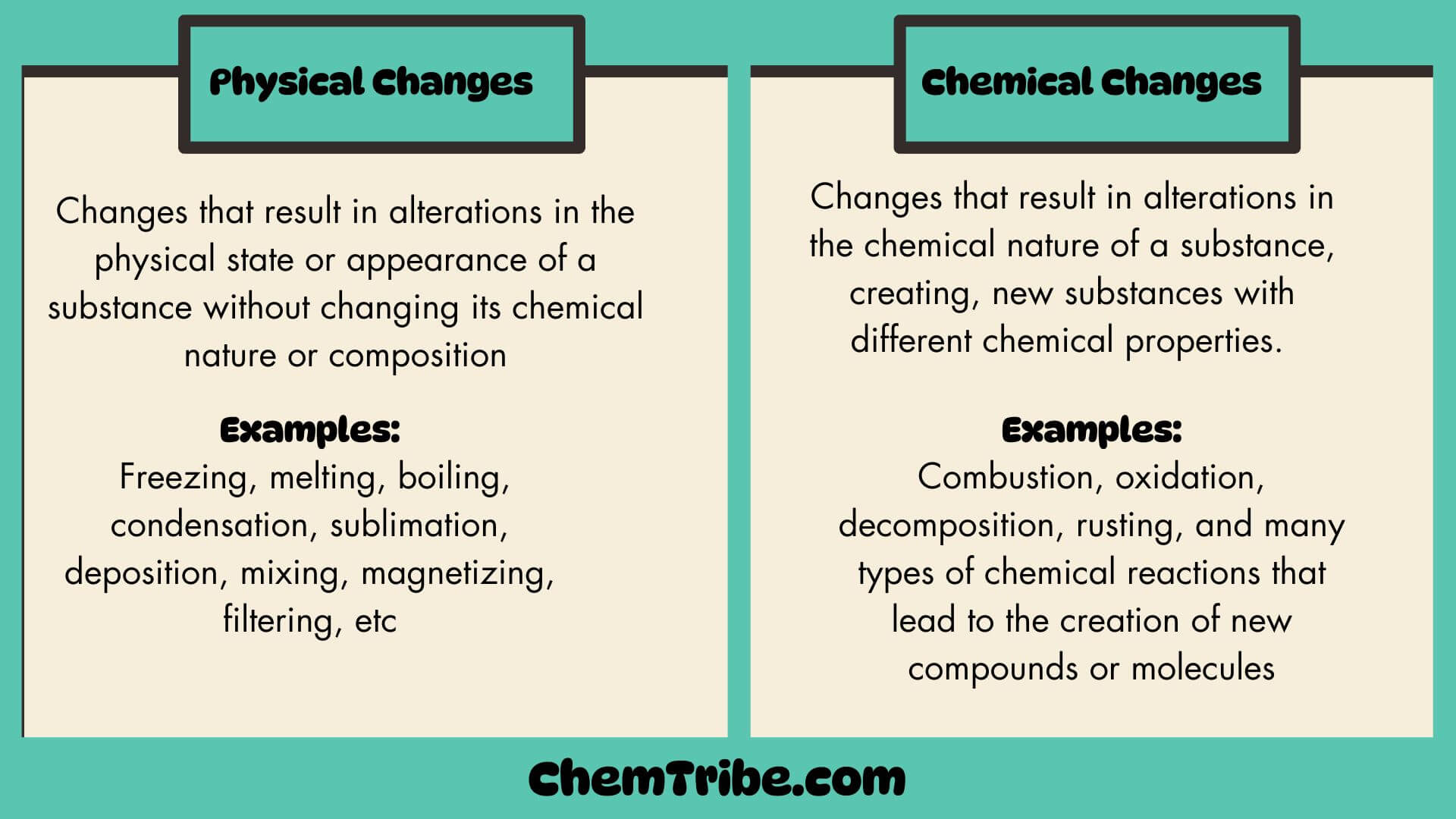
Physical and Chemical Changes
Most substances undergo changes when subjected to different conditions such as heat, cold, pressure, electric current, or contact with other substances. These changes can be categorized into two main groups: physical changes and chemical changes. As a chemist, it is essential to know whether a substance undergoes a physical or chemical change for the following…
-
Criteria of Purity: How to Determine the Purity of a Substance
After learning about different techniques that we can use to separate mixtures into their components, it is necessary to understand how to determine whether the components or a substance we are interested in are pure or impure. The best way to do this is by analyzing one or more of its properties. These properties include…
-
Separation by Centrifugation
Generally, separation by centrifugation is applied in separating mixtures based on differences in density. The process involves spinning a mixture at high speeds in a centrifuge, a machine that rotates rapidly around a central axis. As the mixture spins, centrifugal force is applied, causing the components of the mixture to separate. The denser components move…
-
Magnetic Separation
Magnetic separation is used to separate solid mixtures containing magnetic and non-magnetic components. The separation technique relies on the magnetic properties of certain materials, which allows them to be attracted to magnets. In a magnetic separation process, a mixture containing magnetic and non-magnetic materials is brought closer to a magnetic or a magnetic field. The…