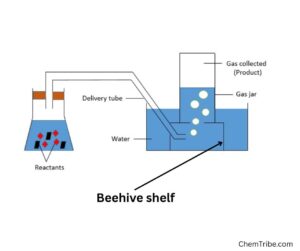
What is a Pneumatic Trough?
A pneumatic trough is a laboratory container used for collecting gases that are insoluble or only slightly soluble in water, such as oxygen, hydrogen, or nitrogen. It is typically made of glass, metal, or plastic and is filled with water to facilitate gas collection.
The principle behind the pneumatic trough is water displacement. When gas is produced in a chemical reaction, it is directed through a delivery tube into a submerged gas collection bottle. As the gas enters, it pushes the water out, allowing the gas to fill the bottle without mixing with air. This method ensures that the collected gas is pure and uncontaminated.
Types of Pneumatic Troughs
Pneumatic troughs come in different designs and materials, each suited for specific laboratory needs. The main types include:
1. Glass Pneumatic Trough

• Made from borosilicate glass, which is resistant to heat and chemical reactions.
• Provides clear visibility, allowing scientists to observe gas collection easily.
• Commonly used in educational and research laboratories.
3. Plastic Pneumatic Trough

• Made from polypropylene or other chemical-resistant plastics.
• Lightweight, affordable, and shatterproof, making it ideal for school laboratories.
• Suitable for basic gas collection experiments but may not handle extreme heat.
Other Uses of Pneumatic Trough
Apart from gas collection, a pneumatic trough has several other laboratory uses. It can serve as a temporary storage container for water or chemical solutions needed in experiments.
In some cases, it is used for sterilizing lab equipment, especially when filled with disinfectant solutions to soak glassware.
Additionally, the trough can function as a drying station for cleaned test tubes, beakers, and other lab ware, allowing excess water to drain off efficiently.