Some of the substances we come across in our daily lives are pure while others are impure. In science, pure means not mixed with anything else.
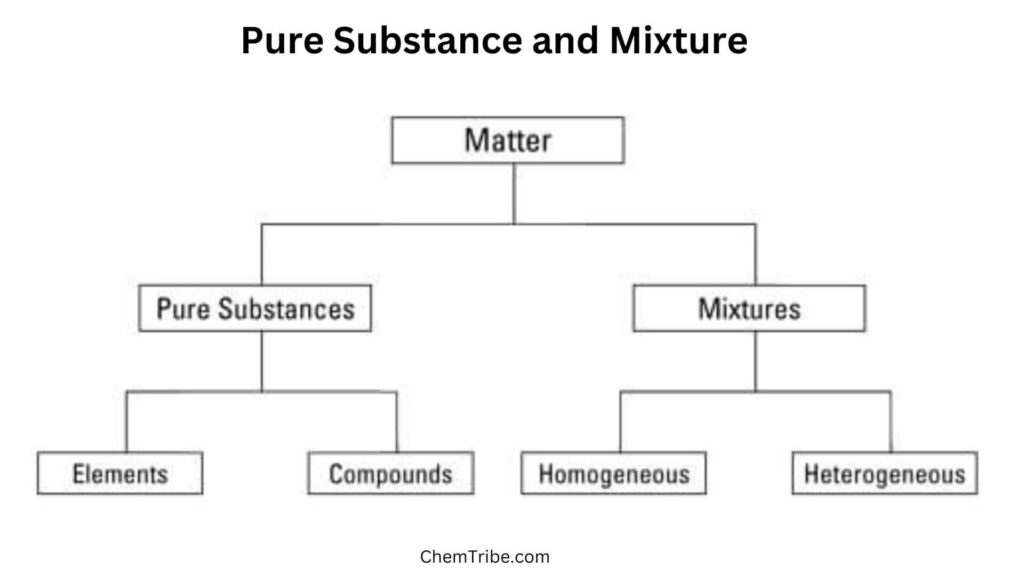
A pure substance has a single type of matter with characteristic chemical properties.
Each pure substance has distinct properties (such as boiling point, melting point, density, etc) that distinguish it from other pure substances. For instance, all samples of pure water regardless of their sources are colourless, freeze at 00C, and boil at 1000C at standard pressure. Elements and compounds are considered to be pure substances.
So, examples of pure substances include common salt, sugar, water, hydrogen, ether, oxygen, carbon dioxide, diamond, gold, silver, baking soda, etc
Most of the substances we across are impure. They consist of two or more pure substances mixed together. As such, they are called mixtures. For instance, air is a mixture because it contains nitrogen, oxygen, carbon (IV) oxide, water vapor, and noble gases. Rocks are also mixtures of various minerals. Seawater is also a mixture as it is a mixture of various salts and water. It is not pure water. Similarly, sugar solution is a mixture of sugar and water while sugar is a pure substance consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in fixed proportions.
A mixture is a combination of two or more substances that are physically blended together but not chemically combined i.e each substance retains its own chemical identity.
Other examples of mixtures are soft drinks, milk, tea, petroleum, ink, cement, rocks, a solution of oil and water, wooden chair, etc.
The different pure substances that make up a mixture, for instance, the individual gases in the air are called components. Each of the components in a mixture retains its specific properties. In a mixture of salt and sand, for instance, the salt retains its solubility in water while sand retains its solubility.
Mixtures are further divided into homogenous and heterogeneous mixtures. Check the subsequent section.
Summary
| Pure Substance | Mixture |
| -Fixed composition -One type of matter -Same properties -Single substance -Cannot be broken down or separated into new products | -No fixed composition -Different types of matter -Overall set of different properties -More than one substance -Can be separated using different separation techniques. |



