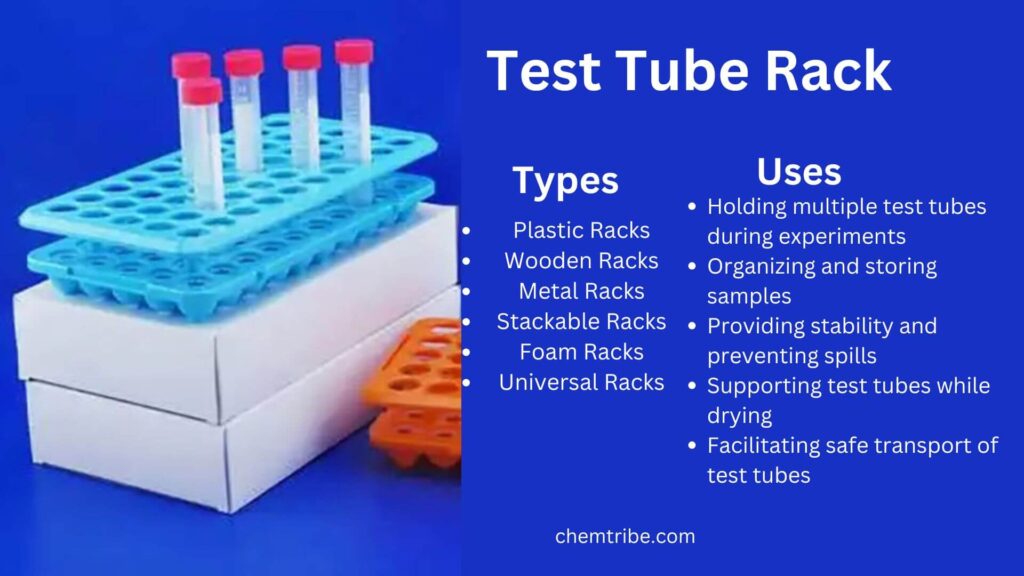
What is a Test Tube Rack?
A test tube rack is a laboratory tool used to hold, organize, and store test tubes safely during experiments. It prevents test tubes from tipping over and spilling their contents. Test tube racks come in different materials, including plastic, wood, and metal.
Types of Test Tube Racks
Test tube racks come in different designs, each suited for specific laboratory needs. The type of rack used depends on factors like material, test tube size, storage requirements, and the nature of the experiment. Below are some of the most common types:

- Plastic Racks – Lightweight, chemical-resistant, and easy to clean. Commonly used in educational labs and research facilities due to their affordability and ease of cleaning.
- Wooden Racks – Sturdy and durable, often used in educational labs. They are often used in schools and general chemistry labs but are less resistant to chemicals and moisture compared to plastic or metal racks.
- Metal Racks – Made of stainless steel or aluminum, resistant to heat and corrosion. They are ideal for high-temperature experiments and environments where chemical resistance is important.
- Floating Racks – Designed to hold test tubes upright in water baths. They are often made from lightweight plastic or foam, ensuring they float securely without tipping over.
- Stackable Racks – Built to save space in busy laboratories, these racks can be stacked on top of each other when not in use. They helps in organizing test tubes efficiently and is useful for long-term sample storage.
- Interlocking Cube Racks –These are racks that consist of multiple small cube-like sections that can be connected or rearranged based on lab needs. They provide flexibility for storing different-sized test tubes in a customizable setup.
- Aluminum Test Tube Racks – Lightweight, durable, and ideal for high-temperature applications. Excellent for experiments requiring high-temperature resistance and long-lasting durability.
- Foam Test Tube Racks – Soft, lightweight racks that hold test tubes securely and prevent breakage. They are useful for transporting fragile samples or working with delicate glassware.
- Universal Racks – These are designed with adjustable slots to hold test tubes of various sizes, making them a versatile option for different experiments. They are ideal for labs that work with multiple tube diameters without needing separate racks for each size.
Uses of Test Tube Racks
Test tube racks play a crucial role in laboratory work by ensuring organization, safety, and efficiency. Below are some key uses of test tube racks:
- Holding Multiple Test Tubes during Experiments: A test tube rack allows scientists to work with several test tubes at once, making it easier to compare samples, conduct experiments, or observe chemical reactions simultaneously. This is especially useful in experiments involving different solutions, serial dilutions, or controlled reactions.
- Organizing and Storing Samples: In research and diagnostic labs, test tube racks help arrange samples in an orderly manner, ensuring they are easily accessible and correctly labeled. This organization is critical for tracking patient samples in medical testing or monitoring ongoing experiments in chemistry and biology labs.
- Providing Stability and Preventing Spills: Test tubes are narrow and prone to tipping over, which can result in spilled chemicals, wasted samples, or hazardous situations. A rack keeps test tubes securely upright, reducing the risk of accidents and contamination.
- Supporting Test Tubes While Drying: After being washed, test tubes need to be dried properly before reuse to avoid contamination or dilution of future samples. Test tube racks provide an organized space for drying, allowing air to circulate around the tubes for faster drying.
- Facilitating Safe Transport of Test Tubes: When moving test tubes from one part of the lab to another, a rack ensures they stay in place and do not break. This is particularly important in clinical labs, research facilities, and fieldwork, where samples need to be carefully transported without spillage or damage.
- Allowing Easy Placement in Incubators, Water Baths, or Refrigerators: Some experiments require temperature control, and test tube racks allow for efficient storage inside incubators, refrigerators, or water baths. Floating test tube racks are specifically designed for immersion in water baths while keeping tubes upright.
- Helping in Heat-Based Experiments: In procedures like DNA amplification, bacterial culture, or chemical heating, test tube racks keep tubes properly positioned inside ovens, autoclaves, or heat blocks.
Test Tube Rack vs. Test Tube Holder
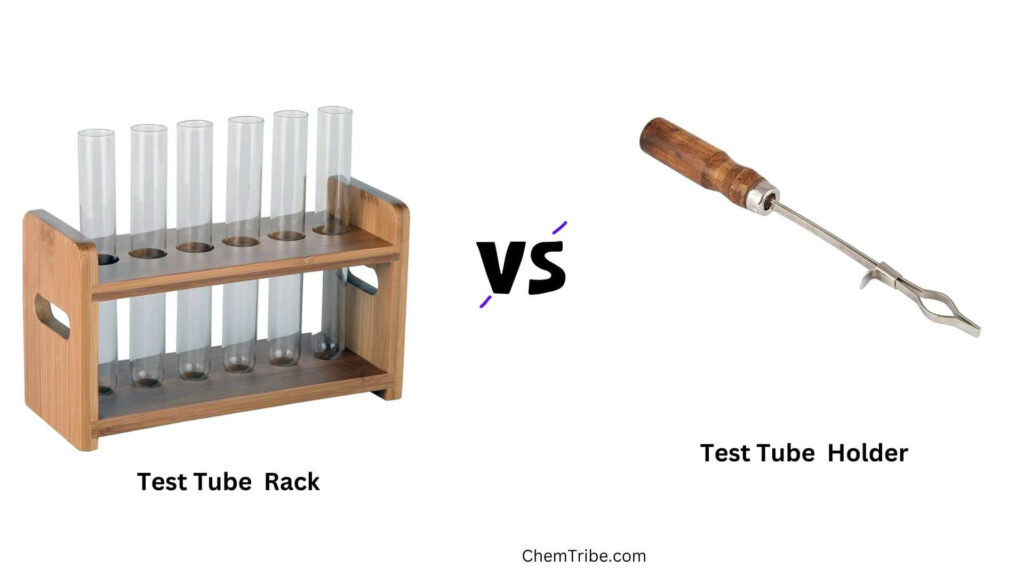
Although people sometimes confuse them, test tube racks and test tube holders serve very different purposes in the lab.
A test tube rack is designed to hold multiple test tubes at once, keeping them upright for easy organization, storage, or transport. Scientists also use racks to dry test tubes after washing, store samples in a refrigerator, or place tubes in an autoclave for sterilization.
A test tube holder, on the other hand, is a handheld tool made for gripping a single test tube. It has spring-loaded jaws that open when you squeeze the handle and close around the test tube when released.
Holders are especially useful when a test tube should not be touched directly, such as when it’s heated over a flame or contains dangerous chemicals. They also help keep a safe distance when transferring liquids or handling substances that might react unpredictably.
Care & Maintenance
Proper maintenance of a test tube rack is essential to ensure its longevity and functionality in the laboratory.
Regular cleaning is necessary to remove any chemical residues, spills, or biological contaminants that may accumulate over time. This helps prevent cross-contamination between experiments and ensures a clean working environment.
Depending on the material of the rack, cleaning methods may vary; for example, plastic and metal racks can be washed with mild detergent and water, while wooden racks should be wiped down to avoid water absorption, which could lead to warping or mold growth.
Storage conditions also play a crucial role in maintaining the rack’s quality. Metal racks should be kept in a dry environment to prevent rusting, while wooden racks should be stored away from moisture to avoid mold formation.
Proper drying after cleaning is important for all types of racks to prevent any buildup of bacteria or fungi.
Additionally, regular inspections should be conducted to check for any cracks, loose parts, or weakened sections that could compromise the rack’s stability.
A damaged test tube rack may cause tubes to tip over, increasing the risk of spills or breakage. If any part of the rack is broken or unstable, it should be repaired or replaced promptly to ensure laboratory safety and efficiency.



