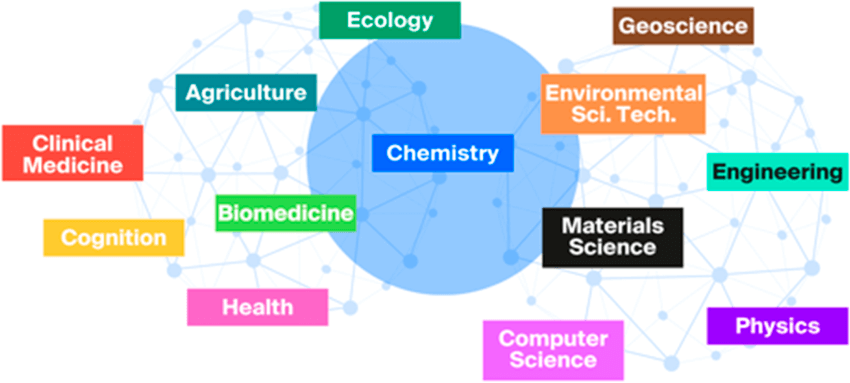
When studying other scientific disciplines, such as biology, physics, geology, agriculture, engineering, medicine, and so forth, you will notice that chemistry is an integral part of your curriculum. This is because chemistry is fundamental to the understanding of these disciplines.
Chemistry serves as a bridge between other scientific disciplines and that’s why it is often referred to as the “central science”.
See, chemistry provides fundamental understanding of matter, its properties, and its interactions, all of which are essential for advancements in a wide range of disciplines. Many scientific phenomena can also be explained through chemical principles, making chemistry a cornerstone of scientific inquiry and innovation.
1. Interdisciplinary Nature
Chemistry’s interdisciplinary nature allows it to serve as a link between several major fields of science. It connects concepts, principles, and methods from various disciplines, including physics, biology, environmental science, and more.
- Physics: Many concepts in physics, such as thermodynamics, quantum mechanics, and atomic theory, have deep connections with chemistry. For instance, understanding chemical bonding requires knowledge of atomic and molecular physics. Chemistry provides the practical application of physical principles like energy conservation and phase transitions in matter.
- Biology: Biology is deeply intertwined with chemistry, particularly in the field of biochemistry, which focuses on chemical processes within living organisms. Every biological function—from digestion to cellular respiration and DNA replication—relies on chemical reactions. Chemistry explains how enzymes catalyze reactions, how proteins fold into functional shapes, and how molecules like glucose and oxygen are involved in cellular processes.
- Environmental Science: Chemistry is also crucial to understanding environmental processes, such as the cycling of nutrients in ecosystems, the behavior of pollutants, and the chemistry of greenhouse gases. For example, understanding how carbon dioxide interacts in the atmosphere (a chemical process) is central to addressing climate change.
2. Foundational to Other Sciences:
Chemistry forms the foundation of many other scientific disciplines by providing fundamental principles that underlie other areas of study. For instance:
- Physics: The study of atomic and molecular physics is rooted in chemistry. Concepts such as electron configuration and the behavior of matter at the atomic level are important for both chemistry and physics. The field of physical chemistry specifically bridges the gap between chemistry and physics by applying the principles of thermodynamics, quantum mechanics, and kinetics to chemical systems.
- Biology: Modern biology is based on a chemical understanding of life. Genetics, for example, relies on the chemistry of DNA and how genetic information is encoded and transmitted. Physiological processes like nerve signaling, muscle contraction, and immune responses depend on chemical interactions between molecules like neurotransmitters, ions, and proteins.
- Geology: The field of geology also relies on chemistry to understand the Earth’s composition, mineral formation, and rock cycle. Chemical analysis of minerals, the behavior of gases in the Earth’s crust, and the study of plate tectonics (which involves the chemistry of Earth’s core) are all critical to understanding geological processes.
3. Understanding Matter
Chemistry is the study of matter, its properties, and how it changes. Understanding these fundamental aspects of matter is essential because all natural and artificial phenomena involve matter in some form, and its behavior can often only be explained through chemistry.
- Properties of Matter: Chemistry helps us understand the physical and chemical properties of materials—such as boiling points, density, and conductivity—which are critical for applications across all sciences. For example, knowledge of the chemical properties of water (such as its polarity and hydrogen bonding) is crucial for understanding its role in biology, environmental science, and even physical chemistry.
- Chemical Changes: Chemistry explains how and why chemical reactions occur, whether it’s the rusting of iron, the combustion of fuel, or the digestion of food in our bodies. These processes are essential for everything from energy production to the functioning of living organisms.
4. Chemical Reactions Are Everywhere
Chemical reactions occur constantly in nature and in all scientific fields. These reactions are at the heart of many important processes, and an understanding of chemistry is essential to comprehending how and why these reactions take place.
- In Nature: Chemical reactions are involved in phenomena like the weathering of rocks, the formation of natural resources, and the cycling of nutrients through ecosystems. The process of photosynthesis in plants, for example, is a chemical reaction that converts light energy into chemical energy, which is essential for life on Earth.
- In Technology: Industrial processes, like the manufacture of steel, the production of energy, or the refining of petroleum, depend on chemical reactions. Similarly, chemical reactions are crucial in modern technologies such as batteries (chemical energy storage), pharmaceuticals (drug synthesis), and even electronics (semiconductor manufacturing).
5. Technological Innovation
Chemistry is at the core of many technological innovations. Advances in materials science, pharmaceuticals, energy production, and environmental sustainability all depend on chemistry.
- Materials Science: The development of new materials—such as semiconductors, superconductors, and nanomaterials—relies on understanding the properties and behavior of atoms and molecules. For example, the invention of plastics, alloys, and ceramics all came about through the application of chemical principles to create substances with desirable properties.
- Pharmaceuticals: The design, synthesis, and production of drugs depend heavily on chemical reactions and interactions at the molecular level. Understanding how drugs interact with the body and how to synthesize new compounds for medical use requires deep knowledge of chemistry. Chemists play a vital role in developing life-saving medicines and vaccines.
- Energy Production: Chemical processes are involved in various energy production methods, including the combustion of fossil fuels, the chemical reactions in batteries, and the process of photosynthesis in plants (which is the basis for bioenergy). Developing sustainable energy sources, such as biofuels, solar cells, and hydrogen energy, also involves applying chemical principles to optimize efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
- Environmental Solutions: Chemistry is essential for addressing environmental challenges like pollution control, waste management, and climate change. For example, the development of catalysts for reducing automobile emissions, the removal of pollutants from water, and the design of renewable energy systems all rely on chemical principles.
Recommended: 55 Examples of Chemistry in Everyday Life
6. Predictive Power:
One of the key strengths of chemistry is its ability to predict the behavior of substances in various conditions. This predictive power is essential for both scientific research and practical applications.
- Reaction Predictions: Chemists can predict how substances will react when mixed together based on their chemical properties and the nature of their bonds. This allows for the design of new materials, drugs, and processes with specific desired outcomes. For example, predicting how different drugs will interact with biological molecules can lead to the development of more effective medications with fewer side effects.
- Environmental Predictions: Chemistry allows scientists to predict how pollutants will behave in the environment. For example, knowing how carbon dioxide reacts in the atmosphere enables predictions about climate change. Similarly, understanding the chemical reactions that take place in soil and water helps in predicting how pollutants will spread or degrade.
- Technology Development: The development of new technologies often involves predicting how new materials will perform under different conditions. For example, the development of advanced materials for electronics, aerospace, or energy storage requires an understanding of how chemical properties will affect performance.
So, Chemistry’s ability to explain the nature of matter, predict reactions, and connect diverse scientific fields makes it the central science that underpins much of our understanding of the natural and technological world. You can think of chemistry as the heart of many other disciplines. Just like your heart pumps blood to your body, chemistry helps other sciences work together.



