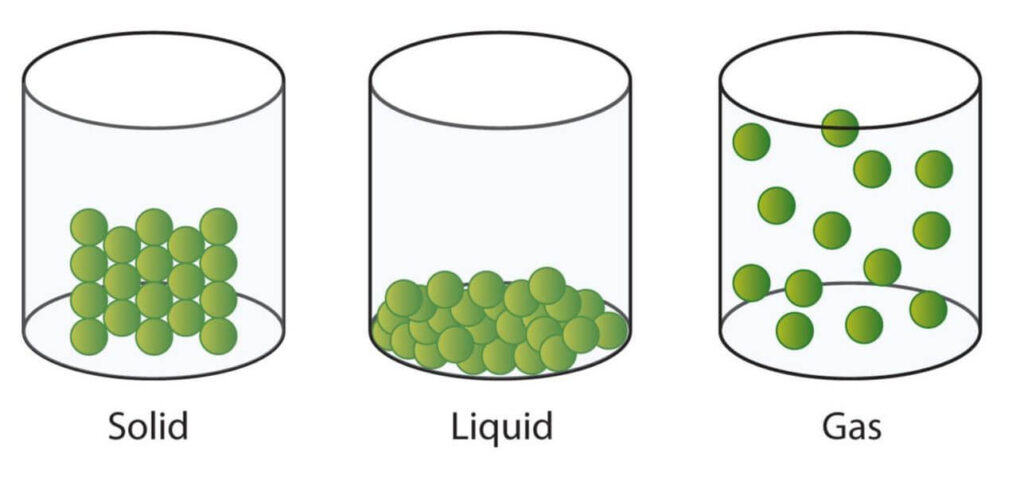
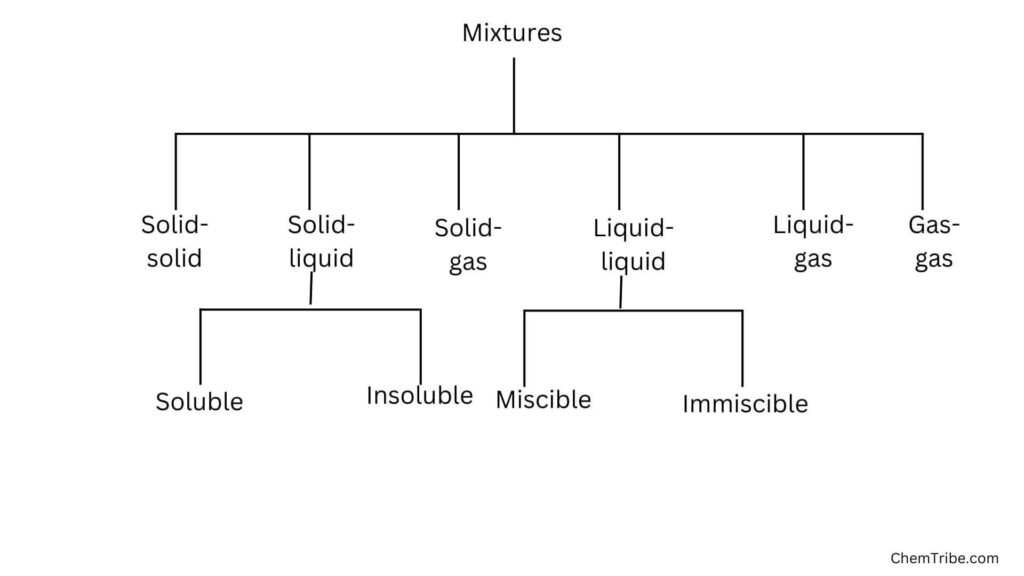
As discussed in the primary states of matter post, matter can be classified into solids, liquids, and gases. In nature, matter exists often as mixtures in various combinations. The flow chart below represents the various categories of mixtures.
Over the years, scientists have attempted to separate the components of various mixtures to obtain pure substances, which are more useful to humans. For instance, they have attempted to remove impurities from water to obtain pure water, which is safe for human consumption.
Reasons for Separating the Components of Mixtures
Why do we need to separate the components of mixtures? Well, we separate components of mixtures for the following reasons:
- To obtain a pure sample of a substance: We need pure substances in our daily lives for various purposes like conducting different experiments in the laboratory and carrying out research work in medicines and other fields.
- To eliminate undesirable or harmful components: Some mixtures may contain undesirable components, some of which may even be harmful. It is necessary to remove such components to retain only the desirable ones. For example, we remove small stones from rice before cooking, as they could potentially harm our teeth.
- To get useful components of mixtures: There are instances when a mixture contains more than one useful component. It is necessary to separate such mixtures for their individual uses. For example, consider a mixture of petroleum. To obtain components such as fuel, oil, petroleum, naphtha, etc., we need to employ an appropriate separation technique.
Methods Used For Separating Components of Mixtures
The methods of separation of mixtures depend on the physical properties of the components contained in a mixture.
Several techniques are available for separating the components of mixtures. The choice of technique to use depends on:
- The type of mixture
- Its physical properties
- The components you are interested in
The type of mixture can be:
| Type of Mixture | Examples |
| Solid-solid mixture | Salt and sand |
| Solid-liquid mixture | Salt and water |
| Liquid-liquid mixture | Water and ethanol |
| Liquid-gas mixture | Water and oxygen |
| Gas-gas mixture | Carbon (IV) oxide, Nitrogen, oxygen, and noble gases |
The physical properties may include:
- Whether the components of the mixture are soluble or insoluble
- Whether the liquids and miscible or immiscible
- Whether the components are magnetic or non-magnetic
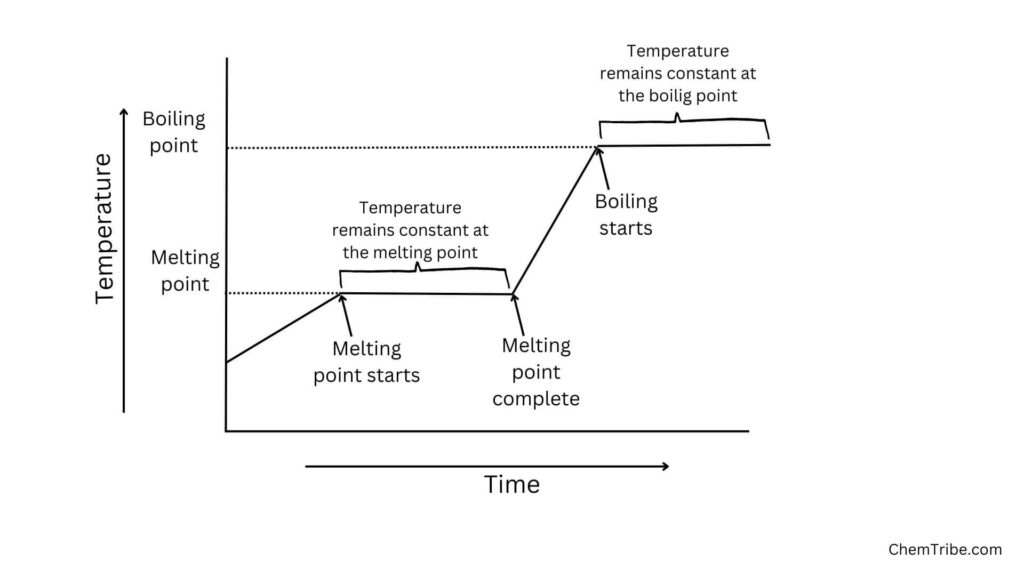
- The melting and boiling points of the components in the mixture
- The densities of the components in the mixture
- Whether the components sublime or not
The Most Common Methods of Separating Mixtures
The following are the most common separation techniques:
1. Separating Solid-Solid Mixtures
| Separation Technique | What it Does | How It Works |
| Winnowing | Separates heavier particles (like grains) from lighter particles (chaff or husks) by tossing them in the air. | |
| Picking | Involves manually removing larger pieces of impurities (such as stones) from a mixture by hand. | |
| Use of magnets | Separates magnetic materials (such as iron) from non-magnetic materials. | Check out this post |
| Sublimation | Separates a mixture by heating it, causing one component to change directly from a solid to a gas, leaving behind the other components. | Check out this post |
2. Separating Solid-Liquid Mixtures
| Separation Technique | What it Does | How It Works |
| Separation of Insoluble Solids from Liquids | ||
| Filtration | Separates an insoluble solid from a liquid or solution by passing it through a filter medium. | Check out this post |
| Decantation | Separates a mixture by carefully pouring off the liquid layer while leaving the solid sediment or precipitate behind. | Check out this post |
| Separation of Soluble Solids from Liquids | ||
| Evaporation | Separates a solvent from a solution by heating the mixture until the solvent evaporates, leaving behind the solute. | Check out this post |
| Crystallization | Separates a solute from a solution by cooling the solution, causing the solute to form crystals that can be easily separated from the liquid. | Check out this post |
3. Separation of Liquid-Liquid Mixtures
| Separation Technique | What it Does | How It Works |
| Separation of Immiscible Liquids | ||
| Using separating funnel | Separates liquids with different densities by allowing them to settle into distinct layers and then draining them through a tap. | Check out this post |
| Using teat pipettes | Transfers small volumes of liquids accurately and precisely, commonly used in titration experiments to deliver precise amounts of titrant or analyte. | |
| Separation of Miscible Liquids | ||
| Simple distillation | Separates components of a mixture based on differences in their boiling points by heating the mixture, then collecting the condensed vapors. | Check out this post |
| Fractional distillation | Separates mixture components with closer boiling points more effectively than simple distillation by employing a fractionating column for enhanced separation efficiency. | Check out this post |
4. Other Separation Methods
| Separation Technique | What it Does | How It Works |
| Chromatography | Separates components of a mixture based on their affinity for a stationary phase and a mobile solvent. | Check out this post |
| Solvent extraction | Separates substances based on their solubility in two immiscible solvents, usually water and an organic solvent. | Check out this post |
| Centrifugation | Separates components of a mixture based on differences in their density by spinning the mixture at high speeds. | Check out this post |
Test Your Knowledge
Summary